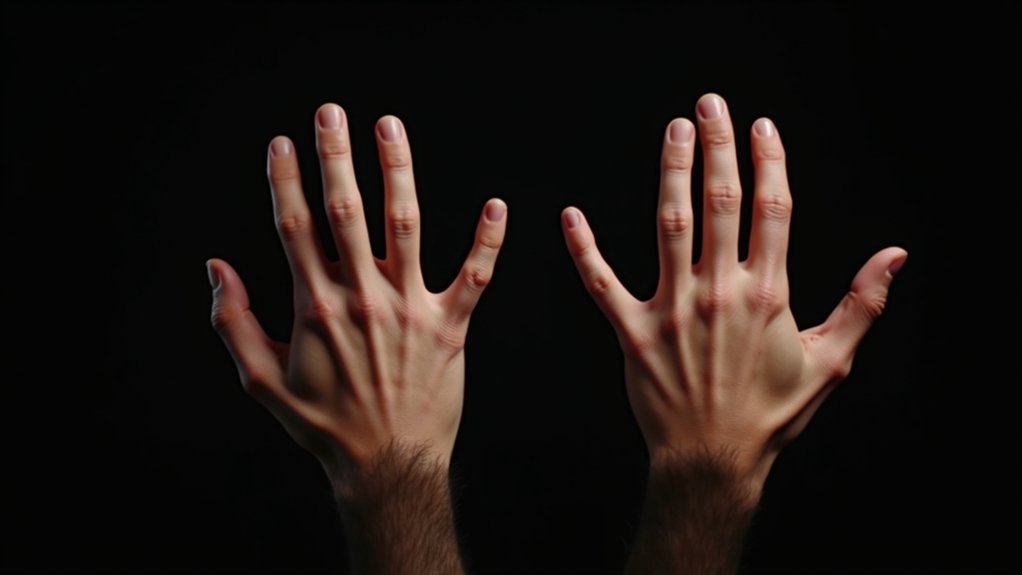
AI struggles to duplicate human hands due to their extreme complexity. With 27 bones, 34 muscles, and over 100 ligaments, hands are remarkably intricate. Current AI systems lack sufficient hand-focused training data, especially 3D models showing proper movement. They can't replicate the 58 distinct movements humans perform or understand spatial relationships between fingers. AI's inability to process tactile feedback and biomechanical nuances leads to common errors like three-fingered distortions. The challenges run deeper than meets the eye.
Despite rapid advances in artificial intelligence technology, AI systems continue to struggle when it comes to accurately depicting human hands. This persistent challenge stems from the remarkable complexity of human hand anatomy. With 27 bones, 34 muscles, and over 100 ligaments and tendons, hands represent one of the body's most intricate structures. The carpal bones arrangement forms a critical foundation for wrist flexibility that AI struggles to model accurately.
AI's difficulty with hands also relates to data limitations. Current datasets lack sufficient hand-focused images, with hands often partially obscured in photos. There's also minimal 3D data showing hand structure and movement across diverse demographics. Without this thorough information, AI systems can't learn the full range of hand variations.
AI struggles with hands due to insufficient training data covering diverse hand structures and movements.
The biomechanical complexity of hands presents another obstacle. Human hands can perform 58 distinct movements, with the opposable thumb being unique to primates. This fine motor control requires precise neural input and complex muscle coordination that AI doesn't fully understand. The frequent appearance of three-finger anomalies in AI-generated images further demonstrates this understanding gap.
AI faces significant perceptual challenges too. Unlike humans, AI lacks tactile feedback for hand interactions and struggles to convert 2D images into accurate 3D structures. This makes it difficult for AI to grasp hand functionality and recognize hand-object relationships.
The variability in human hands further complicates AI's task. Hands differ greatly in size, proportion, skin texture, and color across populations. Age-related changes and individual differences in finger length ratios add more complexity that AI must account for.
Technical limitations also hinder progress. Current AI models often lack true 3D understanding and struggle with spatial relationships. This makes it hard to maintain consistent hand structure or render fine details like wrinkles in generated images.
Finally, AI suffers from a cognitive understanding gap. Unlike humans who intuitively grasp hand biomechanics and functionality, AI has no inherent understanding of what hands do or how they work. This makes it especially difficult for AI to depict hands performing meaningful, contextually appropriate gestures or actions.
Frequently Asked Questions
Will AI Ever Perfectly Replicate Human Hand Dexterity?
Perfect replication of human hand dexterity remains unlikely in the near future. Scientists are making impressive progress with robotic hands that can manipulate objects with increasing skill.
However, the human hand's complex structure with 27 bones and 34 muscles presents major challenges. Recent breakthroughs like ALOHA Released and DEX-EE show promise, but the integration of true proprioception and sensory feedback still lags behind human capabilities.
How Close Is AI to Mimicking Human Finger Sensitivity?
AI is making progress in mimicking human finger sensitivity but still has far to go.
Current sensors can detect tiny forces and identify textures with high accuracy. Meta's system has 8 million sensing points, while BioTac sensors can feel contact points and surface properties.
However, human fingertips have over 3,000 receptors and complex movement capabilities that remain difficult to replicate artificially.
Can Prosthetic Hands Controlled by AI Match Natural Movement?
AI-controlled prosthetic hands are making strides but can't fully match natural movement.
While they achieve 99.2% success in lab tests, they're slower than biological hands with a 0.81 second response time.
Today's prosthetics struggle with fine motor control, precise finger positioning, and realistic force application.
The complex anatomy of human hands—with 27 bones and 34 muscles—remains difficult to duplicate through current AI and mechanical systems.
What Specific Hand Tasks Create the Biggest Challenges for AI?
AI struggles most with tasks requiring fine touch sensitivity and complex dexterity.
Handling delicate objects like eggs or tissues demands precise pressure control that AI can't easily measure.
Tasks combining multiple skills—like threading a needle while holding fabric—overwhelm current systems.
Musical performances present extreme challenges, as they require split-second timing, pressure variations, and emotional interpretation that AI hasn't mastered.
Real-time adaptation to unexpected situations also remains difficult.
Are There Any Hand Functions AI Can Already Perform Better?
AI-powered robotic hands already outperform humans in several areas.
They maintain consistent force application without fatigue during repetitive tasks. These systems achieve submillimeter positioning accuracy and can handle a wider variety of object shapes.
Advanced tactile sensors provide higher resolution touch data than human fingertips. AI also processes sensory information faster than human reaction time, enabling quicker grasp initiation and precise adjustments.









