Virtual reality is transforming pilot training with remarkable efficiency. Studies show VR improves knowledge retention by up to 400% compared to traditional methods. Major airlines like United and agencies including the U.S. Air Force have adopted this technology. VR creates risk-free flight scenarios while reducing costs and carbon emissions. Despite concerns about motion sickness, the global aircraft simulation market is projected to reach $8.95 billion by 2028. The aviation industry’s shift reveals an inevitable technological evolution.
Nearly every aspect of pilot training is being transformed by virtual reality technology. Studies show VR improves knowledge retention by up to 400% compared to traditional methods. This breakthrough is changing how pilots prepare for the skies.
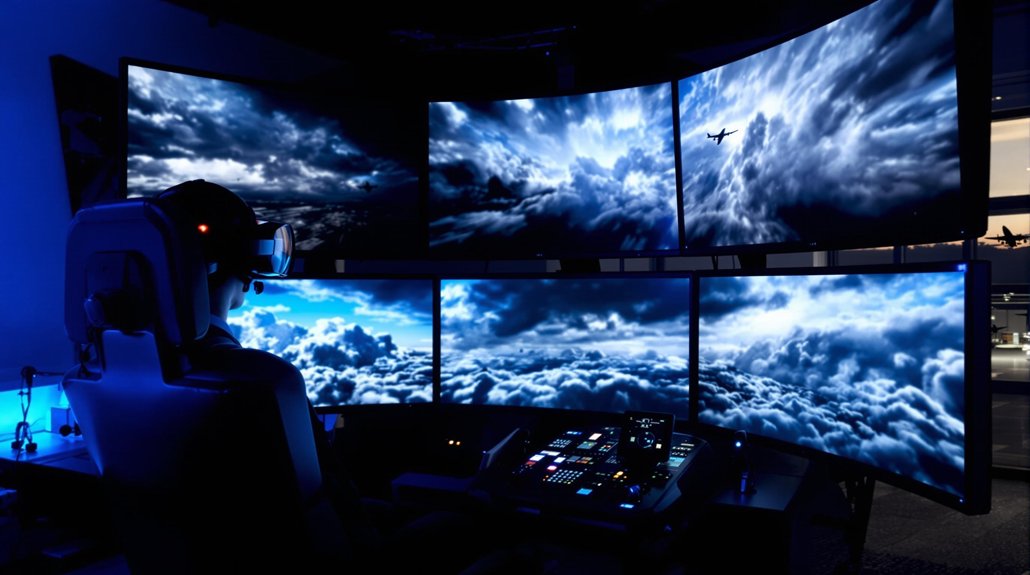
VR creates realistic flight scenarios without the risks or costs of actual flying. Pilots can practice emergency landings, navigate through thunderstorms, and handle equipment failures safely on the ground. They receive immediate feedback on their performance and can repeat challenging scenarios until they master them.
The cost savings are substantial. Airlines spend less on fuel, aircraft maintenance, and instructor fees. VR systems can fit in small spaces, replacing bulky physical simulators. This technology also reduces carbon emissions by decreasing the need for actual flight hours during training.
United Airlines has already incorporated VR into their safety training programs. The European Union Aviation Safety Agency is now certifying VR flight simulators for official pilot training. The U.S. Air Force has launched Project Fusion, using VR to prepare military pilots more efficiently.
The technology employs 360-degree video headsets that immerse pilots in virtual cockpits. Hand controls mimic real aircraft instruments, while AI systems analyze performance and suggest improvements. High-quality graphics create realistic visuals of airports, weather conditions, and airspace.
Training efficiency increases as pilots can practice consistently in diverse environments and aircraft types. VR provides risk-free practice for pilots to master complex maneuvers that would be dangerous in real-world training. They can train remotely and connect with other crew members virtually. The personalized learning approach helps pilots earn their certifications faster. Solutions like VRpilot technology require only a headset and hand controls to provide comprehensive training experiences.
Some challenges remain. There’s concern about negative transfer of learning and motion sickness in some users. The technology requires thorough testing and validation. However, the aviation industry continues to embrace VR as the future of pilot training.
The global aircraft simulation market is expected to reach $8.95 billion by 2028, showing strong confidence in this technology. As VR systems become more advanced, they’ll likely become standard in pilot training programs worldwide.