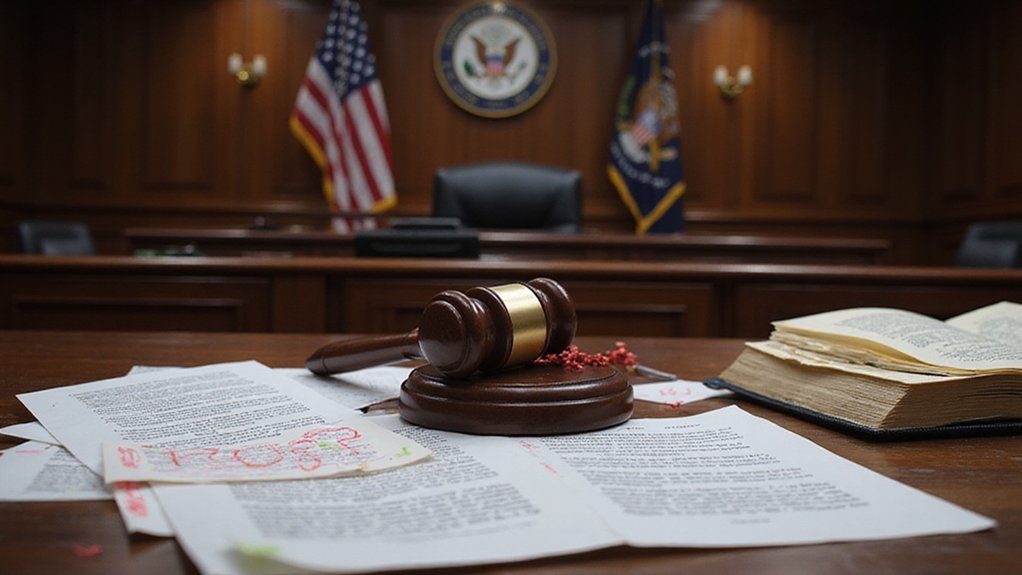
Federal Judge Nina Y. Wang of the District of Colorado issued a scathing order against attorneys representing MyPillow CEO Mike Lindell on April 23, 2025. The judge exposed nearly thirty fake citations in legal briefs submitted to the court in the Coomer v. Lindell defamation case.
The order revealed various citation errors including references to cases that don’t exist, false legal principles attributed to real decisions, and jurisdictional misrepresentations. One example cited “Perkins v. Fed. Fruit & Produce Co.” which was completely fabricated by artificial intelligence.
“These aren’t simple typos,” said Judge Wang in her Order to Show Cause. “They’re a serious breach of professional responsibility that undermines our judicial system.”
This incident isn’t isolated. In May 2025, two additional cases of AI-generated fake citations emerged in court filings. Earlier in February, a major law firm ranked 42nd by headcount faced sanctions for similar AI-related citation errors.
The problems stem from AI hallucinations, where generative models like ChatGPT create convincing but fictional information. The attorneys involved relied on tools like CoCounsel and Google Gemini without proper verification of the generated content. When directly questioned by the court, the defense attorney eventually admitted using AI to draft the legal briefs containing the problematic citations. Attorneys are facing consequences for failing to verify AI output before submitting it to courts. Some lawyers treated AI-generated content as final research rather than a starting point requiring verification.
Courts are now imposing sanctions on attorneys submitting fake citations. Legal experts suggest these incidents qualify as professional misconduct, with some advocating for suspension of responsible lawyers.
“Every time this happens, it sets back legitimate AI adoption in the legal profession,” explained a legal technology expert. “These are clear cautionary tales of what happens when new technology is misused.”
The legal community now recommends multiple verification steps when using AI tools. Rather than accepting AI output at face value, attorneys must confirm information through traditional legal research methods.
The case continues to reverberate through the legal profession as a stark reminder that even powerful AI tools require human oversight, especially in high-stakes legal proceedings where accuracy is paramount.
References
- https://www.lawnext.com/2025/05/ai-hallucinations-strike-again-two-more-cases-where-lawyers-face-judicial-wrath-for-fake-citations.html
- https://natlawreview.com/article/court-slams-lawyers-ai-generated-fake-citations
- https://www.abajournal.com/news/article/no-42-law-firm-by-headcount-could-face-sanctions-over-fake-case-citations-generated-by-chatgpt
- https://www.bclplaw.com/en-US/events-insights-news/fake-legal-authorities-ai-hallucination-or-professional-negligence.html
- https://www.goldbergsegalla.com/news-and-knowledge/news/frank-ramos-warns-attorneys-of-irresponsible-ai-usage-in-texas-lawyer-article/